Understanding Liquidity Pools, AMMs, and Liquidity Mining
Whether you're new to crypto or a seasoned trader, you've probably heard terms like "adding liquidity" or "removing liquidity" in group chats. But what do they actually mean? Today, we’ll break down Liquidity Pools (LP) in a way that even a crypto newbie can understand.
(I bet a pack of spicy strips you’ll get it by the end!)
What is a Market Maker?
Market makers (MMs) originated in traditional stock and commodity exchanges. Back then, retail traders couldn’t directly buy or sell stocks—they had to rely on market makers who provided bid/ask prices to facilitate trades.
Since pricing was done manually, spreads (the difference between buy and sell prices) were huge, and MMs profited from this gap.
With the rise of computerized trading, manual market-making faded, but the core concept remains:
✅ Provide liquidity (ensure assets can be bought/sold easily)
✅ Reduce price spreads (narrow the gap between buy/sell orders)
✅ Stabilize markets (especially in low-liquidity or volatile conditions)
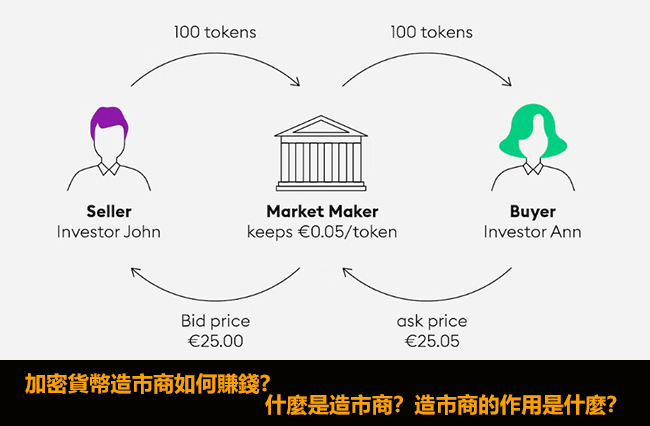
Example: How Market Makers Work
Let’s say gold futures are trading at $2,600 per contract.
- You sell 2 contracts at $2,600, but instead of a real buyer, a market maker takes your order.
- Later, someone buys 2 contracts at 2,600.05∗∗—theMMsellsthemyourcontractsandpocketsthe∗∗2,600.05∗∗—theMMsellsthemyourcontractsandpocketsthe∗∗0.05 spread per unit ($1 total profit).
This happens millions of times per day across markets.
Bonus Insight:
In low-volatility markets, MMs sometimes manipulate prices slightly to trigger stop-losses and create liquidity. If you’ve ever been "hunted" by sudden price spikes/drops, that’s likely an MM bot at work.
What is a Liquidity Pool (LP)?
In centralized exchanges (CEX) like Binance or OKX, market makers ensure smooth trading. But in decentralized exchanges (DEXs), there’s no middleman—so how do trades happen?
CEX vs. DEX Analogy
- CEX = Supermarket → You buy/sell directly with the exchange.
- DEX = Farmers’ Market → You trade peer-to-peer, but need a way to match buyers/sellers.
Solution? Automated Market Makers (AMMs)—a system where smart contracts replace human market makers.
How AMMs Work
Users deposit crypto into a shared pool (LP). Traders then swap tokens directly with the pool, not other users.
Example:
Imagine a DEX as a farmers’ market with a shared shelf (LP).
- To list your token, you must lock equal-value assets (e.g., 100ofyourtoken+100ofyourtoken+100 of USDT).
- This ensures fair pricing and prevents scams.
How Token Prices Move in AMMs
Most AMMs (like Uniswap) use the x × y = k formula:
- x = Token A supply in the pool
- y = Token B supply (e.g., USDT)
- k = Constant product (must stay the same)
Price Change Example
- You create Token A and want it priced at $1.
- You deposit 100 Token A + 100 USDT into the LP.
- Initial price = 1 USDT per Token A.
- Someone buys 10 Token A:
- Pool now has 90 Token A + 110 USDT.
- New price = 110 / 90 = $1.22 (a 22% increase!).
- Another 10 Token A are bought:
- Pool now has 80 Token A + 122.2 USDT.
- New price = 122.2 / 80 = $1.525.
This shows how small trades in low-liquidity pools cause huge price swings!

Liquidity Mining (Bonus Concept)
To stabilize prices, projects incentivize users to add liquidity:
- You stake your tokens in the LP.
- In return, you earn trading fees or rewards (hence "mining").
Why?
- More liquidity → smaller price impact per trade.
- Projects avoid extreme volatility from low liquidity.
Final Thoughts
Now you understand:
🔹 Market Makers (MMs) = Traditional liquidity providers.
🔹 Liquidity Pools (LPs) = Smart contract-based AMM systems.
🔹 Liquidity Mining = Earning rewards for staking in LPs.
With this knowledge, you’ll navigate DeFi like a pro—whether you're trading or launching your own token!
Learn More About CPBOX
Explore features: https://docs.cpbox.io
Suggestions or custom needs?
Contact us:https://www.cpbox.io/cn/
Join Our Community
Telegram Group: https://t.me/cpboxio
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Web3CryptoBox | https://x.com/cpboxio
YouTube: https://youtube.com/channel/UCDcg1zMH4CHTfuwUpGSU-wA